Trigeminal Neuralgia
All Services

Dr. (Maj) Varun Bajaj
MBBS, MD Anaesthesiology
FCPM (MUHS), FIAPM(ISSP)
Director – Devbhoomi Pain Spine Center
Why Choose Us
Our clinic is the first to offer world class comprehensive pain management services in Uttarakhand. All our procedures are : *Non surgical, *Painless, *Less than 1 hour duration, *Done under imaging guidance, *Performed by experienced professionals
Latest Blog
Would You Like to know ?
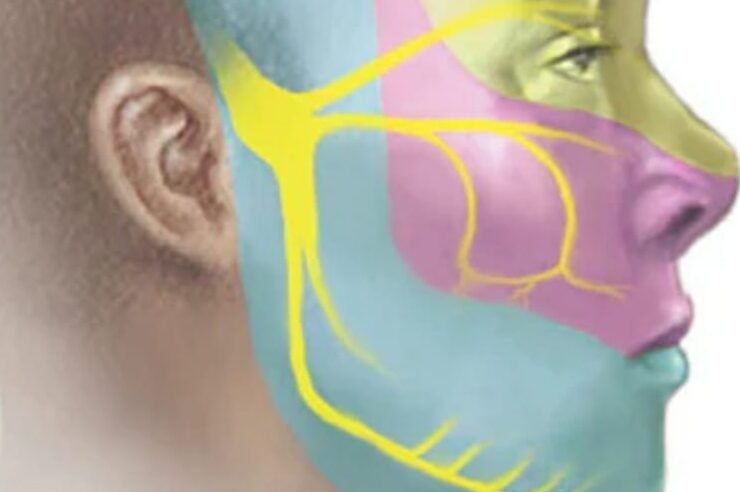
About Trigeminal Neuralgia
It is characterized by intense sudden electrical pain which may be accompanied by muscular spasms on the affected side of the face.
The pain of TN occurs on the right side of the face more often than the left.
Would You Like to know ?
Treatment, Recognition & Prevention
Differential diagnosis:
- Multiple sclerosis
- Glossopharyngeal neuralgia
- Cluster headache
- Trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias
- Tolosa hunt syndrome
- Herpes zoster
What is the purpose of pain intervention?
Pain management interventions are specifically tailored according to the patient needs after proper investigation and conservative treatment with commonly available medications.
Interventions help the patient to decrease pain medication and break pain cycle so that patient can resume day to day activities
Pain intervention options:
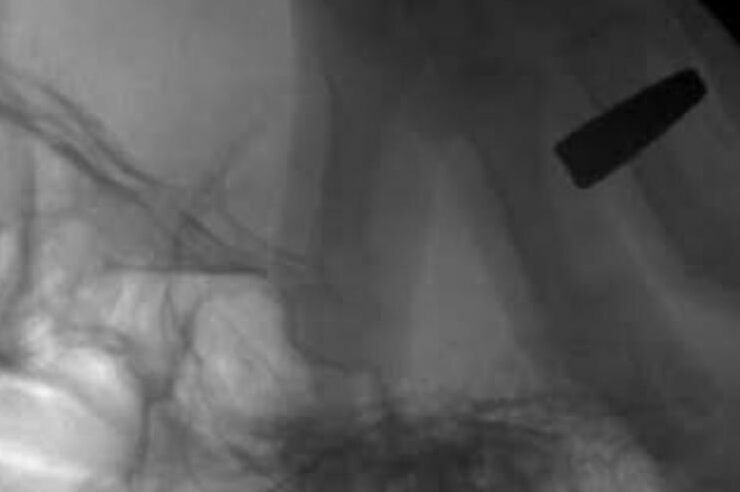
Imaging guided blocks
- Supraorbital nerve block
- Mental nerve block
- Mandibular nerve block
- Maxillary nerve block
- Botulinum toxin injections
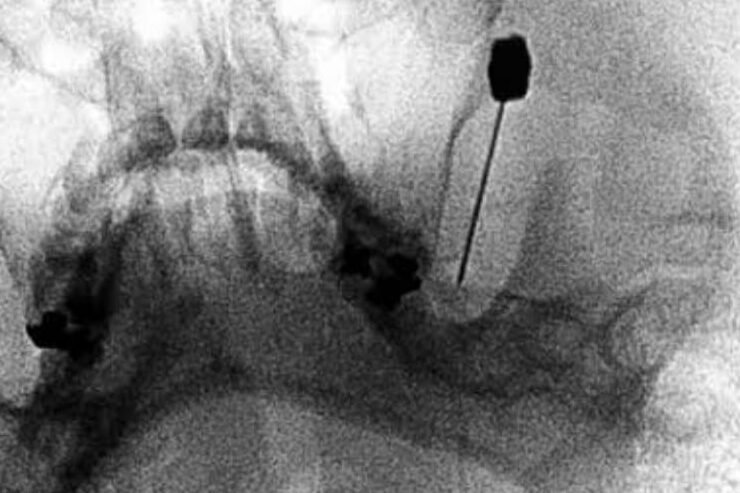
Radiofrequency ablation
- RFA trigeminal ganglion
- Pain: Can vary in intensity and location, from sharp and sudden to dull and chronic.
- Swelling: Indication of inflammation or injury.
- Stiffness: Reduced range of motion.
- Redness and Warmth: Common with infections or inflammatory conditions.
- Instability: The knee may feel like it could give way.
- Crunching or Popping Sounds: Can be indicative of cartilage damage or ligament issues.
Self-Care:
- Rest: Avoid activities that aggravate the knee pain.
- Ice: Apply ice packs to reduce swelling.
- Compression: Use knee braces or wraps.
- Elevation: Keep the knee raised to reduce swelling.
Medications:
- Pain Relievers: NSAIDs (e.g., ibuprofen) to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: Injections to reduce severe inflammation.
Physical Therapy:
- Exercises: Strengthening and stretching exercises to support the knee.
- Manual Therapy: Techniques to improve mobility and reduce pain.
Surgery:
- Arthroscopy: Minimally invasive surgery to repair or remove damaged tissue.
- Partial or Total Knee Replacement: For severe arthritis or damage.
Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture: Some find relief through acupuncture.
- Supplements: Glucosamine and chondroitin may help some individuals.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Reduces stress on the knees.
- Stay Active: Regular exercise strengthens muscles around the knee.
- Warm-Up: Proper warm-up before activities.
- Proper Gear: Use appropriate shoes and equipment for activities.


